MAPS performance: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Anemosadmin (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Definitions == | == Definitions == | ||
=== Accuracy === | |||
Accuracy measures how close the result is to the actual value we were trying to achieve. The accuracy values shown below are based on our simulated tests. | |||
=== Precision === | === Precision === | ||
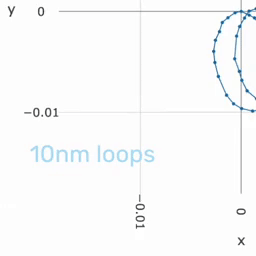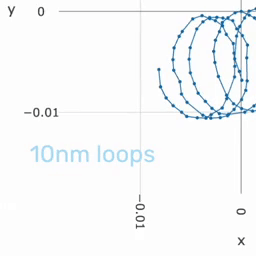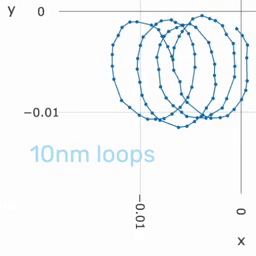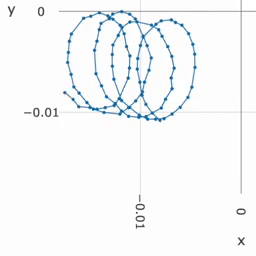
Precision measures the consistency of our system and gives information about the relative accuracy in application. High precision is enough if achieving a high global accuracy is not needed but to measure the degree of displacement. | |||
=== Resolution === | === Resolution === | ||
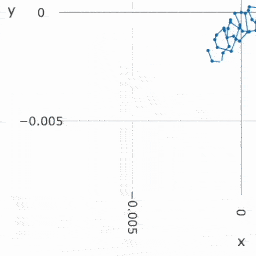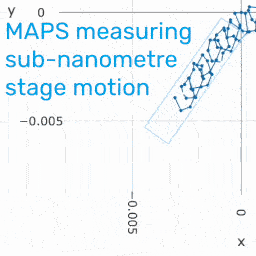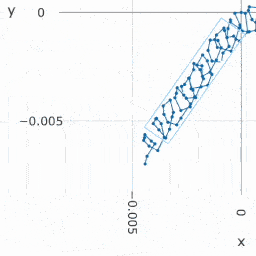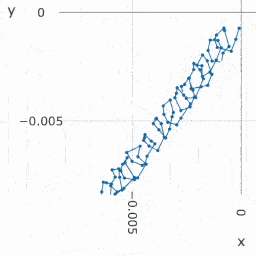
Resolution shows the theoretical accuracy of our system, i.e. the absolute limit of the technology. | |||
=== Noise floor === | === Noise floor === | ||
Noise floor measures the degree of change in a stationary state. | |||
=== Repeatability === | === Repeatability === | ||
Repeatability shows how close are the different measurement results to each other, comparing the results of the NPL (National Physical Laboratory), our real tests and our simulated tests. | |||
=== Conditions === | === Conditions === | ||
Revision as of 14:33, 29 November 2023
Sensor performance criteria quoted industry-wide are often ill defined or plain misleading. MAPS performance is assessed in several ways, each with different utility. These specifications are explained here.
Definitions
Accuracy
Accuracy measures how close the result is to the actual value we were trying to achieve. The accuracy values shown below are based on our simulated tests.
Precision
Precision measures the consistency of our system and gives information about the relative accuracy in application. High precision is enough if achieving a high global accuracy is not needed but to measure the degree of displacement.
Resolution
Resolution shows the theoretical accuracy of our system, i.e. the absolute limit of the technology.
Noise floor
Noise floor measures the degree of change in a stationary state.
Repeatability
Repeatability shows how close are the different measurement results to each other, comparing the results of the NPL (National Physical Laboratory), our real tests and our simulated tests.
Conditions
accuracy, resolution, repeatability, noise floor.